|
Not all systems are the same. They solve different problems, need different business domains and technical environments,
have different requirements for reliability, safety, etc. and have different systems maintenance lifecycles. You need a Systems
Development Model that can cover all of these situations, yet allow you to deliver and maintain these systems within the cost
and schedule constraints you define. Heinsights
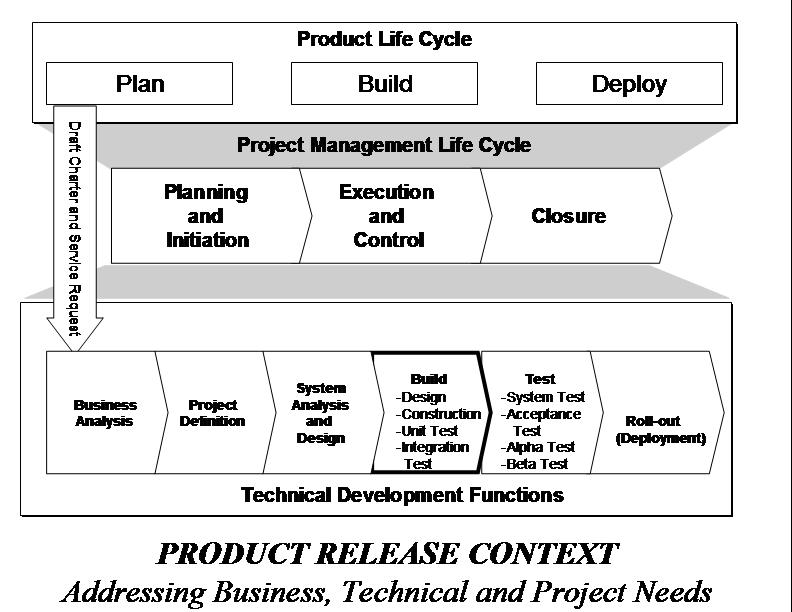
uses a Product Development Context (defined below) that allows us to effectively consider the systems (product) business
aspects (including the product lifecycle), the project management aspects, and the technical system development aspects in
an integrated fashion. This provides us the ability to examine your current situation and recommend improvements – resulting
in a SDM tailored for you. It is important to note that the Project Management Life Cycle (PMLC) and Product Life Cycle (PLC)
and the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) drive repositories of reusable methods that can be selected and integrated to
meet the demands of projects varying in size and complexity.
The SDM we provide is a framework for system development and maintenance and includes:
·
A Methodology – a logically related set of functions that are performed systematically to develop and maintain your systems (products). Typically,
these functions (phases) include system conceptualization/definition, analysis, design, construction, test, and deployment.
The methodology consists of a set of methods (processes) that are performed during specific phases. For example there may
be multiple conceptualization, analysis/design (e.g., object oriented analysis & design, structured analysis and design,
etc.), quality assurance methods, etc. The methodology also includes processes that are performed across all phases, e.g.,
project control, configuration management, verification & validation. The methodology is described in terms of formalized
process definitions – including inputs, tasks, deliverable and roles and responsibilities. The process definitions may
conform to industry or your own standards and modeling semantics.
·
Methods - processes for accomplishing specific systems development objectives. Examples
can include those specified above and also processes such as estimation, costing, scheduling, requirements definition and
management, reviews, inspections, data modeling, process modeling, prototyping and many more.
·
A Systems Development Life Cycle
(SDLC) - Organized and integrated steps
for project management and technical systems development (steps for the production of a system from initial formulation of
the problem through operation). The SDLC is organized into phases of development, the specific methods used within and across
phases, the sequencing of these phases, the iteration within and between these phases, and the major milestones and deliverables
from these phases. Many industry models such as the waterfall, spiral, fountain, iterative and incremental models, or a combination
of these are candidates to become part of your SDM.
·
Tools Support – technology products (tools developed by you internally
or by industry vendors) used to support and automate the processes used in the methodology. Multiple industry tool choices
exist for most methods.
|
